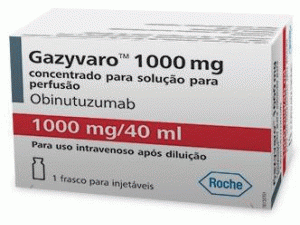
奥比妥珠单抗冻干粉注射剂(Gazyvaro 1000mg/40mL)
 产地国家:瑞士
处方药:是
所属类别: 1000毫克/40毫升/瓶
包装规格: 1000毫克/40毫升/瓶
计价单位:瓶
生产厂家英文名:Roche Pharma (Schweiz) AG
原产地英文商品名:Gazyvaro 1000mg/40mL/Vial
原产地英文药品名:obinutuzumab
中文参考商品译名:Gazyvaro冻干粉 1000毫克/40毫升/瓶
中文参考药品译名:奥比妥珠单抗
产地国家:瑞士
处方药:是
所属类别: 1000毫克/40毫升/瓶
包装规格: 1000毫克/40毫升/瓶
计价单位:瓶
生产厂家英文名:Roche Pharma (Schweiz) AG
原产地英文商品名:Gazyvaro 1000mg/40mL/Vial
原产地英文药品名:obinutuzumab
中文参考商品译名:Gazyvaro冻干粉 1000毫克/40毫升/瓶
中文参考药品译名:奥比妥珠单抗
简介
2014年7月30日,欧盟委员会已批准罗氏公司的 Gazyvaro(obinutuzumab)与苯达莫司汀化疗联合使用于接受 Gazyvaro 持续治疗的滤泡性淋巴瘤患者。这次批准适用的患者是在单独使用美罗华(利妥昔单抗)或含美罗华的治疗方案进行治疗后,仍然未见疗效甚至疾病继续恶化的群体。 这次批准是基于一项名为加多林的三期研究结果,该研究表明单独使用 Gazyvaro 后以 Gazyvaro 联合苯达莫司汀治疗,可导致疾病恶化或死亡(无进展生存,PFS)的风险降低 52%,对照组为单独使用苯达莫司汀。 该研究由一个独立的审查委员会(IRC)评估,根据评审人员的评估结果,Gazyvaro 联合治疗组相比单独用苯达莫司汀治疗组其中位 PFS 高出一倍以上(29.2 个月对比 13.7 个月),此外,Gazyvaro 联合治疗组的患者相比苯达莫司汀单独治疗组的患者其死亡的风险降低了 38%。罗氏首席医疗官和全球产品开发负责人 Horning 对这次批准评论道:今天的批准对欧洲的滤泡性淋巴瘤患者来说是一次显著的里程碑。对于使用美罗华治疗但仍无法控制病情的患者来说,Gazyvaro 联合苯达莫司汀是一个重要的新方案,这个选择已被证实能够使疾病进展或死亡的风险降低一半以上。 有了这次审批,Gazyvaro 现在在欧洲已经获得批准用于治疗两种常见类型的血癌。 此前,Gazyvaro 与苯丁酸氮芥的联合治疗方案被核准用于初治慢性淋巴细胞白血病(CLL)且应并发症不适合全剂量氟达拉滨治疗方案的患者。这项批准基于关键的 CLL11 试验数据,该试验直接比较了 Gazyvaro 联合苯丁酸氮芥,美罗华 / 利妥昔单抗联合苯丁酸氮芥,以及单独使用苯丁酸氮芥三种治疗方案,Gazyvaro 的组合方案表现出明显的疗效优势。 关于Gazyvaro(obinutuzumab):obinutuzumab在美国的商品名为Gazyva,已获FDA批准,联合苯丁酸氮芥(chlorambucil)化疗,用于既往未经治疗的慢性淋巴细胞白血病(CLL)患者。Gazyva的获批,将减少生物仿制药对罗氏重磅药物美罗华(Rituxan,通用名:rituximab,利妥昔单抗)的冲击。obinutuzumab又名GA101,是首个糖基化的II型抗CD20单克隆抗体,靶向B细胞表面的CD20分子,能够直接诱导B细胞死亡。英文版说明书
obinutuzumab Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity,ADCC Direct Cell Death induction。Gazyvaro 1,000 mg concentrate for solution for infusionIndicationsGAZYVA® (obinutuzumab), in combination with chlorambucil, is indicated for the treatment of patients with previously untreated chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL).GAZYVA® (obinutuzumab), in combination with bendamustine followed by GAZYVA monotherapy, is indicated for the treatment of patients with follicular lymphoma (FL) who relapsed after, or are refractory to, a rituximab-containing regimen.IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATIONBoxed WARNINGS: HEPATITIS B VIRUS REACTIVATION AND PROGRESSIVE MULTIFOCAL LEUKOENCEPHALOPATHY•Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) reactivation, in some cases resulting in fulminant hepatitis, hepatic failure, and death, can occur in patients receiving CD20-directed cytolytic antibodies, including GAZYVA. Screen all patients for HBV infection before treatment initiation. Monitor HBV positive patients during and after treatment with GAZYVA. Discontinue GAZYVA and concomitant medications in the event of HBV reactivation•Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy (PML) including fatal PML, can occur in patients receiving GAZYVAHepatitis B Virus Reactivation•Hepatitis B virus (HBV) reactivation, in some cases resulting in fulminant hepatitis, hepatic failure, and death, can occur in patients treated with anti-CD20 antibodies including GAZYVA. HBV reactivation has been reported in patients who are hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) positive and in patients who are HBsAg negative but are hepatitis B core antibody (anti-HBc) positive. Reactivation has also occurred in patients who appear to have resolved hepatitis B infection (ie, HBsAg negative, anti-HBc positive, and hepatitis B surface antibody [anti-HBs] positive)•HBV reactivation is defined as an abrupt increase in HBV replication manifesting as a rapid increase in serum HBV DNA level, or detection of HBsAg in a person who was previously HBsAg negative and anti-HBc positive. Reactivation of HBV replication is often followed by hepatitis, ie, increase in transaminase levels and, in severe cases, increase in bilirubin levels, liver failure, and death•Screen all patients for HBV infection by measuring HBsAg and anti-HBc before initiating treatment with GAZYVA. For patients who show evidence of hepatitis B infection (HBsAg positive [regardless of antibody status] or HBsAg negative but anti-HBc positive), consult physicians with expertise in managing hepatitis B regarding monitoring and consideration for HBV antiviral therapy•Monitor patients with evidence of current or prior HBV infection for clinical and laboratory signs of hepatitis or HBV reactivation during and for several months following treatment with GAZYVA•In patients who develop reactivation of HBV while receiving GAZYVA, immediately discontinue GAZYVA and any concomitant chemotherapy and institute appropriate treatment. Resumption of GAZYVA in patients whose HBV reactivation resolves should be discussed with physicians with expertise in managing hepatitis B. Insufficient data exist regarding the safety of resuming GAZYVA in patients who develop HBV reactivationProgressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy (PML)•JC virus infection resulting in PML, which can be fatal, was observed in patients treated with GAZYVA. Consider the diagnosis of PML in any patient presenting with new onset or changes to preexisting neurologic manifestations. eva luation of PML includes, but is not limited to, consultation with a neurologist, brain MRI, and lumbar puncture. Discontinue GAZYVA therapy and consider discontinuation or reduction of any concomitant chemotherapy or immunosuppressive therapy in patients who develop PMLInfusion Reactions•GAZYVA can cause severe and life-threatening infusion reactions. Sixty-five percent of patients with CLL experienced a reaction to the first 1000 mg infused of GAZYVA and 38% of patients with iNHL experienced a reaction on Day 1 during treatment with GAZYVA in combination with bendamustine. Infusion reactions can also occur with subsequent infusions. Symptoms may include hypotension, tachycardia, dyspnea, and respiratory symptoms (eg, bronchospasm, larynx and throat irritation, wheezing, and laryngeal edema). Most frequently reported symptoms include nausea, fatigue, dizziness, vomiting, diarrhea, hypertension, flushing, headache, pyrexia, and chills•Premedicate patients with acetaminophen, an antihistamine, and a glucocorticoid. Institute medical management for infusion reactions as needed. Closely monitor patients during the entire infusion. Infusion reactions within 24 hours of receiving GAZYVA have occurred•For patients with any Grade 4 infusion reactions, including but not limited to anaphylaxis, acute life-threatening respiratory symptoms, or other life-threatening infusion reaction: Stop the GAZYVA infusion. Permanently discontinue GAZYVA therapy•For patients with Grade 1, 2, or 3 infusion reactions: Interrupt GAZYVA for Grade 3 reactions until resolution of symptoms. Interrupt or reduce the rate of the infusion for Grade 1 or 2 reactions and manage symptoms•For patients with preexisting cardiac or pulmonary conditions, monitor more frequently throughout the infusion and the post-infusion period since they may be at greater risk of experiencing more severe reactions. Hypotension may occur as part of the GAZYVA infusion reaction. Consider withholding antihypertensive treatments for 12 hours prior to and during each GAZYVA infusion, and for the first hour after administration until blood pressure is stable. For patients at increased risk of hypertensive crisis, consider the benefits versus the risks of withholding their antihypertensive medicationTumor Lysis Syndrome (TLS)•Tumor lysis syndrome, including fatal cases, has been reported in patients receiving GAZYVA. Patients with high tumor burden, high circulating lymphocyte count (>25 x 109/L) or renal impairment are at greater risk for TLS and should receive appropriate tumor lysis prophylaxis with antihyperuricemics (eg, allopurinol or rasburicase) and hydration prior to the infusion of GAZYVA. During the initial days of GAZYVA treatment, monitor the laboratory parameters of patients considered at risk for TLS. For treatment of TLS, correct electrolyte abnormalities, monitor renal function and fluid balance, and administer supportive care, including dialysis as indicatedInfections•Serious bacterial, fungal, and new or reactivated viral infections can occur during and following GAZYVA therapy. Fatal infections have been reported with GAZYVA. Do not administer GAZYVA to patients with an active infection. Patients with a history of recurring or chronic infections may be at increased risk of infectionNeutropenia•Severe and life-threatening neutropenia, including febrile neutropenia, has been reported during treatment with GAZYVA. Patients with Grade 3 to 4 neutropenia should be monitored frequently with regular laboratory tests until resolution. Anticipate, eva luate, and treat any symptoms or signs of developing infection. Consider administration of granulocyte colony-stimulating factors (G-CSF) in patients with Grade 3 or 4 neutropenia•Neutropenia can also be of late onset (occurring more than 28 days after completion of treatment) and/or prolonged (lasting longer than 28 days)•Consider dose delays in the case of Grade 3 or 4 neutropenia. Patients with severe and long lasting (> 1 week) neutropenia are strongly recommended to receive antimicrobial prophylaxis until resolution of neutropenia to Grade 1 or 2. Antiviral and antifungal prophylaxis should be consideredThrombocytopenia•Severe and life-threatening thrombocytopenia has been reported during treatment with GAZYVA in combination with chlorambucil or bendamustine. Fatal hemorrhagic events during Cycle 1 have also been reported in patients with CLL treated with GAZYVA. Monitor all patients frequently for thrombocytopenia and hemorrhagic events, especially during the first cycle. In patients with Grade 3 or 4 thrombocytopenia, monitor platelet counts more frequently until resolution and consider subsequent dose delays of GAZYVA and chemotherapy or dose reductions of chemotherapy. Transfusion of blood products (ie, platelet transfusion) may be necessary. Consider withholding concomitant medications which may increase bleeding risk (eg, platelet inhibitors or anticoagulants), especially during the first cycleImmunization•The safety and efficacy of immunization with live or attenuated viral vaccines during or following GAZYVA therapy have not been studied. Immunization with live virus vaccines is not recommended during treatment and until B-cell recoveryPregnancy•There are no data with GAZYVA use in pregnant women to inform a drug-associated risk. GAZYVA is likely to cause fetal B-cell depletion. GAZYVA should be used during pregnancy and/or breastfeeding only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus and/or infant. Mothers who have been exposed to GAZYVA during pregnancy should discuss the safety and timing of live virus vaccinations for their infants with their child’s healthcare providersGeriatric Use•Of 336 patients with previously untreated CLL who received GAZYVA in combination with chlorambucil, 81% were 65 years and older, while 46% were 75 and older. Of the patients 75 years and older, 46% experienced serious adverse events and 7% experienced adverse events leading to death. Of the patients younger than 75, 33% experienced a serious adverse event and 2% an adverse event leading to death. No significant differences in efficacy were observed between younger and older patients•Of 194 patients with iNHL treated with GAZYVA plus bendamustine, 44% were 65 and over, while 14% were 75 and over. In patients 65 and over, 52% of patients experienced serious adverse events and 26% experienced adverse events leading to treatment withdrawal while in patients under 65, 28% and 12% experienced serious adverse events and adverse events leading to treatment withdrawal, respectively. No clinically meaningful differences in efficacy were observed between these patients and younger patientsAdditional Important Safety InformationCLL•Grade 3/4 adverse reactions in CLL were: neutropenia (33%), infusion reactions (20%), thrombocytopenia (10%), anemia (4%), leukopenia (4%), diarrhea (2%), urinary tract infection (1%), pyrexia (<1%), cough (<1%), and nasopharyngitis (<1%)•The most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥10%) in CLL were: infusion reactions (66%), neutropenia (38%), thrombocytopenia (14%), nausea (12%), anemia (11%), pyrexia (10%), cough (10%), and diarrhea (10%)•Adverse reactions rates and laboratory abnormalities from the Stage 2 phase are consistent with the rates in Stage 1. In addition to the adverse reactions observed in Stage 2, in Stage 1 back pain (5% vs. 2%), anemia (12% vs. 10%) and cough (10% vs. 7%) were observed at a higher incidence in the GAZYVA treated patients. The incidence of Grade 3-4 back pain (<1% vs. 0%), cough (0% vs. <1%) and anemia (5% vs. 4%) was similar in both treatment arms. With regard to laboratory abnormalities, in Stage 1 hyperkalemia (33% vs. 18%), creatinine increased (30% vs. 20%) and alkaline phosphatase increased (18% vs. 11%) were observed at a higher incidence in patients treated with GAZYVA with similar incidences of Grade 3-4 abnormalities between the two armsiNHL•The safety of GAZYVA was eva luated based on a safety population of 392 patients with indolent NHL (iNHL), of whom 81% had follicular lymphoma. In patients with follicular lymphoma, the most common adverse reactions that were seen were consistent with the overall population who had iNHL•Grade 3/4 adverse reactions in iNHL were: neutropenia (33%), infusion reactions (11%), thrombocytopenia (10%), urinary tract infection (3%), upper respiratory tract infection (2%), pyrexia (1%), asthenia (1%), sinusitis (1%), and pain in extremity (1%)•The most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥10%) in iNHL were: infusion reactions (69%), neutropenia (35%), nausea (54%), fatigue (39%), cough (26%), diarrhea (27%), constipation (19%), pyrexia (18%), thrombocytopenia (15%), vomiting (22%), upper respiratory tract infection (13%), decreased appetite (18%), arthralgia (12%), sinusitis (12%), anemia (12%), asthenia (11%), and urinary tract infection (10%)•During the monotherapy period with GAZYVA, the most common Grade 3-4 adverse reactions in iNHL were neutropenia (10%), and anemia, febrile neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, sepsis, upper respiratory tract infection, and urinary tract infection (all at 1%)•During the monotherapy period with GAZYVA, the most common adverse reactions in iNHL patients were cough (15%), upper respiratory tract infections (12%), neutropenia (11%), sinusitis (10%), diarrhea (8%), infusion related reactions (8%), nausea (8%), fatigue (8%), bronchitis (7%), arthralgia (7%), pyrexia (6%), nasopharyngitis (6%), and urinary tract infections (6%)用药温馨提示:当您服用此药物时,需定期接受医疗专业人士的检查,以便随时针对其药效、副作用等情况进行监测。本网站所包含的信息旨在为患者提供帮助,不能代替医学建议和治疗。
药品价格查询,专业药品查询网站,药品说明书查询,药品比价 » 奥比妥珠单抗冻干粉注射剂(Gazyvaro 1000mg/40mL)
药品价格查询,专业药品查询网站,药品说明书查询,药品比价 » 奥比妥珠单抗冻干粉注射剂(Gazyvaro 1000mg/40mL)