催产素注射液Syntocinon 10ui/ml Amps(Oxytocin )说明书
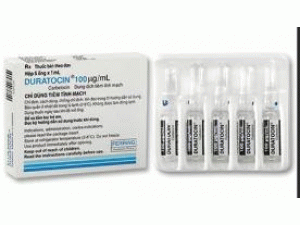
[caption id="attachment_26411" align="alignleft" width="300"]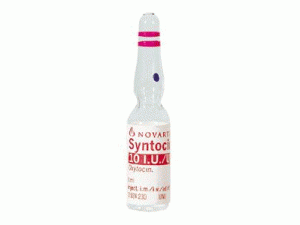 Syntocinon 10ui/ml Amps(Oxytocin 催产素注射液)[/caption]
药店国别:
产地国家:美国
处 方 药:是
所属类别:10单位/毫升/安培 10安培/盒
包装规格:10单位/毫升/安培 10安培/盒
计价单位:盒
生产厂家中文参考译名:Novartis
生产厂家英文名:Novartis
原产地英文商品名:Syntocinon 10iu/ml/amps 10amps/box
原产地英文药品名:Oxytocin
中文参考商品译名:Syntocinon 10单位/毫升/安培 10安培/盒
中文参考药品译名:催产素
Syntocinon 10ui/ml Amps(Oxytocin 催产素注射液)[/caption]
药店国别:
产地国家:美国
处 方 药:是
所属类别:10单位/毫升/安培 10安培/盒
包装规格:10单位/毫升/安培 10安培/盒
计价单位:盒
生产厂家中文参考译名:Novartis
生产厂家英文名:Novartis
原产地英文商品名:Syntocinon 10iu/ml/amps 10amps/box
原产地英文药品名:Oxytocin
中文参考商品译名:Syntocinon 10单位/毫升/安培 10安培/盒
中文参考药品译名:催产素
 Syntocinon 10ui/ml Amps(Oxytocin 催产素注射液)[/caption]
药店国别:
产地国家:美国
处 方 药:是
所属类别:10单位/毫升/安培 10安培/盒
包装规格:10单位/毫升/安培 10安培/盒
计价单位:盒
生产厂家中文参考译名:Novartis
生产厂家英文名:Novartis
原产地英文商品名:Syntocinon 10iu/ml/amps 10amps/box
原产地英文药品名:Oxytocin
中文参考商品译名:Syntocinon 10单位/毫升/安培 10安培/盒
中文参考药品译名:催产素
Syntocinon 10ui/ml Amps(Oxytocin 催产素注射液)[/caption]
药店国别:
产地国家:美国
处 方 药:是
所属类别:10单位/毫升/安培 10安培/盒
包装规格:10单位/毫升/安培 10安培/盒
计价单位:盒
生产厂家中文参考译名:Novartis
生产厂家英文名:Novartis
原产地英文商品名:Syntocinon 10iu/ml/amps 10amps/box
原产地英文药品名:Oxytocin
中文参考商品译名:Syntocinon 10单位/毫升/安培 10安培/盒
中文参考药品译名:催产素
简介
部份中文催产素处方资料(仅供参考) 缩宫素(Oxytocin) 别名:催产素、Pitocin。 作用和用途: 能直接兴奋子宫平滑肌,使子宫收缩。小剂量时,使妊娠末期子宫体产生节律性收缩,使子宫颈平滑肌松弛,促使胎儿顺利娩出。大剂量时引起子宫平滑肌的强直收缩,压迫肌纤维间血管而止血。口服易被消化液所破坏,注射时作用迅速,但维持时间不长。用于引产、催产、防治产后出血。 剂量与用法: 引产和催产:静滴,2.5-5u/次,加入5%葡萄糖液500ml内缓慢滴注。 防治产后出血:肌注,5-10u/次,极量20u/次,也可加于5%葡萄糖中静滴。 不良反应: 剖宫产术中宫体注射有致呼吸困难者。 过敏反应:表现为胸闷、憋气、寒战、发热、心慌、高热寒战(达41℃)、口周发绀、血压下降。 药物过量:剂量过大、滴速太快,可是子宫强直性收缩而致胎儿窒息、胎盘早期剥离或子宫破裂。 注意事项: 骨盆过窄、产道受阻、明显头盆不称及横位产者禁用。 动脉粥样硬化者、心脏病、三胎以上产妇禁用。 有剖腹产史,子宫肌瘤剔除术史及臀位产者慎用。 药物相互作用:缩宫素与甲氧胺同用时,会引起血压升高及严重头痛英文版说明
Generic Name: oxytocin Dosage Form: Injection, USP Syntocinon® Syntocinon® (oxytocin) injection, USP Caution: Federal law prohibits dispensing without prescription. Syntocinon Description Syntocinon® (oxytocin) is a synthetic, (1-6) cyclic nonapeptide. Chemically, oxytocin is designated as Glycinamide, L-cysteinyl-L-tyrosyl-L-isoleucyl-L-glutaminyl-L-asparaginyl-L-cysteinyl-L-prolyl- L-leucy1-, cyclic (1-6)-disulfide. The structural formula is: Syntocinon® (oxytocin) injection is provided as a sterile solution for intravenous or intramuscular administration. Each 1 mL of solution contains 10 USP or International Units of oxytocin and the following inactive ingredients: acetic acid, NF, qs to ....................... pH 4 ± 0.3 alcohol, USP............................ 0.61 % by vol. chlorobutanol, NF ..........,................... 0.5% sodium acetate, USP ...,........................ 1 mg sodium chloride, USP ........................ 0.017 mg water for injection, USP, qs to ..................... 1 mL Syntocinon - Clinical Pharmacology The pharmacologic and clinical properties of Syntocinon® (oxytocin) are identical with the naturally occurring oxytocic principle of the posterior lobe of the pituitary. Syntocinon® (oxytocin) injection does not contain the amino acids characteristic of vasopressin, and therefore has fewer and less severe cardiovascular effects. Syntocinon® (oxytocin) exerts a selective action on the smooth musculature of the uterus, particularly toward the end of pregnancy, during labor and immediately following delivery. Oxytocin stimulates rhythmic contractions of the uterus, increases the frequency of existing contractions, and raises the tone of the uterine musculature. Syntocinon® (oxytocin), when given in appropriate doses during pregnancy, is capable of eliciting graded increases in uterine motility from a moderate increase in the rate and force of spontaneous motor activity to sustained tetanic contraction. Syntocinon® (oxytocin) is promptly effective after parenteral administration. Following intramuscular injection, the myotonic effect on the uterus appears in 3-7 minutes, and persists for 30-60 minutes. With intravenous injection, the uterine effect appears within 1 minute and is of more brief duration. Indications and Usage for Syntocinon Important Notice Syntocinon® (oxytocin) injection is indicated for the medical rather than the elective induction of labor. Available data and information are inadequate to define the benefits to risk considerations in the use of the drug product for elective induction. Elective induction of labor is defined as the initiation of labor for convenience in an individual with a term pregnancy who is free of medical indications. Antepartum Syntocinon® (oxytocin) is indicated for the initiation or improvement of uterine contractions, where this is desirable and considered suitable, in order to achieve early vaginal delivery for fetal or maternal reasons. It is indicated for (1) induction of labor in patients with a medical indication for the initiation of labor, such as Rh problems, maternal diabetes, pre-eclampsia at or near term, when delivery is in the best interest of mother and fetus or when membranes are prematurely ruptured and delivery is indicated; (2) stimulation or reinforcement of labor, as in selected cases of uterine inertia; (3) as adjunctive therapy in the management of incomplete or inevitable abortion. In the first trimester, curettage is generally considered primary therapy. In the second trimester abortion, oxytocin infusion will often be successful in emptying the uterus. Other means of therapy, however, may be required in such cases. Postpartum Syntocinon® (oxytocin) injection is indicated to produce uterine contractions during the third stage of labor and to control postpartum bleeding or hemorrhage. Contraindications Syntocinon® (oxytocin) injection is contraindicated in any of the following conditions: Significant cephalopelvic disproportion; unfavorable fetal positions or presentations which are undeliverable without conversion prior to delivery (transverse lies); i.e., in obstetrical emergencies where the benefit-to-risk ratio for either the fetus or the mother favors surgical intervention; in cases of fetal distress where delivery is not imminent; prolonged use in uterine inertia or severe toxemia; hypertonic uterine patterns; patients with hypersensitivity to the drug; induction or augmentation of labor in those cases where vaginal delivery is contraindicated, such as cord presentation or prolapse, total placental previa, and vasa previa. Warnings Syntocinon® (oxytocin), when given for induction or stimulation of labor, must be administered only by the intravenous route and with adequate medical supervision in a hospital. Precautions General All patients receiving intravenous oxytocin must he under continuous observation by trained personnel with a thorough knowledge of the drug and qualified to identify complications. A physician qualified to manage any complications should be immediately available. When properly administered, oxytocin should stimulate uterine contractions similar to those seen in normal labor. Overstimulation of the uterus by improper administration can be hazardous to both mother and fetus. Even with proper administration and adequate supervision, hypertonic contractions can occur in patients whose uteri are hypersensitive to oxytocin. Except in unusual circumstances, oxytocin should not be administered in the following conditions: prematurity, borderline cephalopelvic disproportion, previous major surgery on the cervix or uterus including cesarean section, over-distention of the uterus, grand multiparity, or invasive cervical carcinoma. Because of the variability of the combinations of factors which may be present in the conditions listed above, the definition of “unusual circumstances” must be left to the judgment of the physician. The decision can only be made by carefully weighing the potential benefits which oxytocin can provide in a given case against rare but definite potential for the drug to produce hypertonicity or tetanic spasm. Maternal deaths due to hypertensive episodes, subarachnoid hemorrhage, rupture of the uterus, and fetal deaths due to various causes have been reported associated with the use of parenteral oxytocic drugs for induction of labor or for augmentation in the first and second stages of labor. Oxytocin has been shown to have an intrinsic antidiuretic effect, acting to increase water reabsorption from the glomerular filtrate. Consideration should, therefore, be given to the possibility of water intoxication, particularly when oxytocin is administered continuously by infusion and the patient is receiving fluids by mouth. Drug Interactions Severe hypertension has been reported when oxytocin was given 3-4 hours following prophylactic administration of a vasoconstrictor in conjunction with caudal block anesthesia. Cyclopropane anesthesia may modify oxytocin's cardiovascular effects, so as to produce unexpected results such as hypotension. Maternal sinus bradycardia with abnormal atrioventricular rhythms has also been noted when oxytocin was used concomitantly with cyclopropane anesthesia. Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility There are no animal or human studies on the carcinogenicity and mutagenicity of this drug, nor is there any information on its effect on fertility. Pregnancy Teratogenic Effects: Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with oxytocin. There are no known indications for use in the first trimester of pregnancy other than in relation to spontaneous or induced abortion. Based on the wide experience with this drug and its chemical structure and pharmacological properties, it would not be expected to present a risk of fetal abnormalities when used as indicated. Nonteratogenic Effects: See ADVERSE REACTIONS in the fetus or infant. Labor and Delivery See INDICATIONS AND USAGE. Nursing Mothers Syntocinon® (oxytocin) may be found in small quantities in mother's milk. If a patient requires the drug postpartum to control severe bleeding, she should not commence nursing until the day after Syntocinon® (oxytocin) has been discontinued. Pediatric Use Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established. Adverse Reactions The following adverse reactions have been reported in the mother: Anaphylactic reaction, Postpartum hemorrhage, Cardiac arrhythmia, Fatal afibrinogenemia, Nausea, Vomiting, Premature ventricular contractions, and Pelvic hematoma. Excessive dosage or hypersensitivity to the drug may result in uterine hypertonicity, spasm, tetanic contraction, or rupture of the uterus. The possibility of increased blood loss and afibrinogenemia should be kept in mind when administering the drug. Severe water intoxication with convulsions and coma has occurred, associated with a slow oxytocin infusion over a 24-hour period. Maternal death due to oxytocin-induced water intoxication has been reported. The following adverse reactions have been reported in the fetus or infant: Due to induced uterine motility: Bradycardia, Premature ventricular contractions and other arrhythmias, Permanent CNS or brain damage, and Fetal death. Due to use of oxytocin in the mother: Low Apgar scores at 5 minutes. Neonatal jaundice, and Neonatal retinal hemorrhage. Drug Abuse and Dependence There is no evidence that Syntocinon® (oxytocin) has been abused or has provoked drug dependence. Overdosage Overdosage with oxytocin depends essentially on uterine hyperactivity, whether or not due to hypersensitivity to this agent. Hyperstimulation with strong (hypertonic) or prolonged (tetanic) contractions, or a resting tone of 15-20 mm H2O or more between contractions can lead to tumultuous labor, uterine rupture, cervical and vaginal lacerations, postpartum hemorrhage, uteroplacental hypoperfusion, and variable deceleration of fetal heart, fetal hypoxia, hypercapnia, or death. Water intoxication with convulsions, which is caused by the inherent antidiuretic effect of oxytocin, is a serious complication that may occur if large doses (40-50 mL/minute) are infused for long periods. Treatment of water intoxication consists of discontinuation of oxytocin, restriction of fluid intake, diuresis, IV hypertonic saline solution, correction of electrolyte imbalance, control of convulsions with judicious use of a barbiturate, and special nursing care for the comatose patient. Syntocinon Dosage and Administration Dosage of oxytocin is determined by uterine response. The following dosage information is based upon the various regimens and indications in general use. Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, wherever solution and container permit. A. Induction of Stimulation of Labor Intravenous infusion (drip method) is the only acceptable method of administration for the induction or stimulation of labor. Accurate control of the rate of infusion flow is essential. An infusion pump or other such device and frequent monitoring of strength of contractions and fetal heart rate are necessary for the safe administration of oxytocin for the induction or stimulation of labor. If uterine contractions become too powerful, the infusion can be abruptly stopped, and oxytocin stimulation of the uterine musculature will soon wane. An intravenous infusion of non-oxytocin containing solution should be started. Physiologic electrolyte solution should be used except under unusual circumstances. To prepare the usual solution for infusion, the contents of one 1-mL ampul are combined aseptically with 1,000 mL of non-hydrating diluent. The combined solution, rotated in the infusion bottle to insure thorough mixing, contains 10 mU/mL. Add the container with dilute oxytocin solution to the system through use of a constant infusion pump or other such device, to control accurately the rate of infusion. The initial dose should be no more than 1-2 mU/minute. The dose may be gradually increased in increments of no more than 1-2 mU/minute, until a contraction pattern has been established which is similar to norma1 labor. The fetal heart rate, resting uterine tone, and the frequency, duration, and force of contractions should be monitored. The oxytocin infusion should be discontinued immediately in the event of uterine hyperactivity or fetal distress. Oxygen should be administered to the mother. The mother and the fetus must be eva luated by the responsible physician. B. Control of Postpartum Uterine Bleeding Intravenous Infusion (Drip Method): To control postpartum bleeding, 10-40 units of oxytocin may be added to 1,000 mL of a non-hydrating diluent and run at a rate necessary to control uterine atony. Intramuscular Administration: 1 mL (10 units) of oxytocin can be given after delivery of the placenta. C. Treatment of Incomplete or Inevitable Abortion Intravenous infusion with physiologic saline solution, 500 mL, or 5% dextrose in physiologic saline solution to which 10 units of Syntocinon® (oxytocin) have been added should be infused at a rate of 20-40 drops/minute. How is Syntocinon Supplied Syntocinon® (oxytocin) injection, USP Available as a 1 mL sterile ampul containing 10 USP or International Units of oxytocin. SandoPak® unit dose packages of 50 ampuls (NDC 0078-0060-04). Store and dispense Below 77ºF (25ºC); DO NOT FREEZE.用药温馨提示:当您服用此药物时,需定期接受医疗专业人士的检查,以便随时针对其药效、副作用等情况进行监测。本网站所包含的信息旨在为患者提供帮助,不能代替医学建议和治疗。
药品价格查询,专业药品查询网站,药品说明书查询,药品比价 » 催产素注射液Syntocinon 10ui/ml Amps(Oxytocin )说明书
药品价格查询,专业药品查询网站,药品说明书查询,药品比价 » 催产素注射液Syntocinon 10ui/ml Amps(Oxytocin )说明书