索拉非尼片Nexavar 200mg Tablets(Sorafenib)
 药店国别:
产地国家:美国
处方药:是
所属类别: 200毫克/片 120片/瓶
包装规格: 200毫克/片 120片/瓶
计价单位:瓶
生产厂家中文参考译名:
生产厂家英文名:Bayer HealthCare AG
原产地英文商品名:NEXAVAR 200MG/Tablets 120Tablets/bottle
原产地英文药品名:SORAFENIB
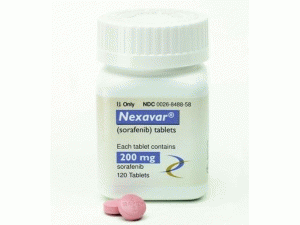
中文参考商品译名:多吉美片 200毫克/片 120片/瓶
中文参考药品译名:索拉非尼
曾用名:
简介:部分中文索拉非尼处方资料(仅供参考)英文药名: Nexavar(Sorafenib Tablets)中文药名: 多吉美(索拉非尼片)生产厂家: Bayer Corp.药品名称商品名:多吉美通用名:甲苯磺酸索拉非尼片英文商品名:Nexavar英文通用名:Sorafenib Tablet性状: 本品为红色圆形片。
适应症
索拉非尼已被批准用于治疗晚期肾细胞癌(最常见的肾癌类型)。此外,目前世界各地还有近50项应用索拉非尼治疗其他多种癌症的各类临床试验正在进行之中。
用法用量
索拉非尼为一种红色、薄膜衣片剂,规格为每片200mg。索拉非尼治疗肾细胞癌的推荐剂量为400mg,每天2次,不可与食物同服(宜在进食1小时前或进食2小时后服药)。制药厂商建议,除非索拉非尼疗效降低或患者不能耐受其毒性反应,否则该药可以一直长期使用。若患者出现药物不良反应,索拉非尼给药剂量可降低到400mg,每天1次或隔天1次。任何疑问,请遵医嘱!用药提示患者在服药之前应仔细阅读产品说明书及患者须知。应告知患者在服药期间必须采取有效避孕措施,以及在停药至少2周之后方可尝试怀孕。告知患者最好空腹服药。若患者忘记服药,下一次服药时也无需加大剂量。当患者在服药期间出现手足部皮疹,应及时联络医生进行相应处理。Nexavar是首个获FDA批准专门用于放射性碘(RAI)难治性分化型甲状腺癌的药物2013年11月25日,口服多激酶抑制剂多吉美(Nexavar,通用名:sorafenib,索拉非尼)已获FDA批准,用于局部晚期或转移性放射性碘(RAI)难治性分化型甲状腺癌的治疗。
索拉非尼片英文版说明书
NEXAVAR is indicated for the treatment of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).NEXAVAR is indicated for the treatment of patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC).NEXAVAR is indicated for the treatment of patients with locally recurrent or metastatic, progressive, differentiated thyroid carcinoma (DTC) that is refractory to radioactive iodine treatment.Important Safety ConsiderationsNEXAVAR is contraindicated in patients with known severe hypersensitivity to sorafenib or any other component of NEXAVARNEXAVAR in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel is contraindicated in patients with squamous cell lung cancerCardiac ischemia and/or myocardial infarction may occur. The incidence of cardiac ischemia/infarction in NEXAVAR-treated vs placebo-treated patients was 2.7% vs 1.3%, 2.9% vs 0.4%, and 1.9% vs 0% in the HCC, RCC, and DTC studies, respectively. Temporary or permanent discontinuation of NEXAVAR should be considered in patients who develop cardiac ischemia and/or myocardial infarctionAn increased risk of bleeding may occur following NEXAVAR administration. The following bleeding adverse reactions were reported in the NEXAVAR-treated vs placebo-treated patients, respectively, in the HCC study: bleeding from esophageal varices (2.4% vs 4%) and bleeding with fatal outcome at any site (2.4% vs 4%); in the RCC study: bleeding regardless of causality (15.3% vs 8.2%), Grade 3 bleeding (2.0% vs 1.3%), Grade 4 bleeding (0% vs 0.2%), and one fatal hemorrhage in each treatment group; in the DTC study: bleeding (17.4% vs 9.6%) and Grade 3 bleeding (1% vs 1.4%). There was no Grade 4 bleeding reported and there was one fatal hemorrhage in a placebo-treated patient. If bleeding necessitates medical intervention, consider permanent discontinuation of NEXAVAR. Due to the potential risk of bleeding, tracheal, bronchial, and esophageal infiltration should be treated with local therapy prior to administering NEXAVAR in patients with DTCMonitor blood pressure weekly during the first 6 weeks and periodically thereafter, and treat, if required. In the HCC study, hypertension was reported in approximately 9.4% of NEXAVAR-treated patients and 4.3% of patients in the placebo-treated group. In the RCC study, hypertension was reported in approximately 16.9% of NEXAVAR-treated patients and 1.8% of patients in the placebo-treated group. In the DTC study, hypertension was reported in 40.6% of NEXAVAR-treated patients and 12.4% of the placebo-treated patients. Hypertension was usually mild to moderate, occurred early in the course of treatment, and was managed with standard antihypertensive therapy. In cases of severe or persistent hypertension despite institution of antihypertensive therapy, consider temporary or permanent discontinuation of NEXAVARHand-foot skin reaction and rash are the most common adverse reactions attributed to NEXAVAR. Management may include topical therapies for symptomatic relief. In cases of any severe or persistent adverse reactions, temporary treatment interruption, dose modification, or permanent discontinuation of NEXAVAR should be considered. There have been reports of severe dermatologic toxicities, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN). These cases may be life-threatening. Discontinue NEXAVAR if SJS or TEN are suspectedGastrointestinal perforation was an uncommon adverse reaction and has been reported in less than 1% of patients taking NEXAVAR. Discontinue NEXAVAR in the event of a gastrointestinal perforationInfrequent bleeding or elevations in the International Normalized Ratio (INR) have been reported in some patients taking warfarin while on NEXAVAR. Monitor patients taking concomitant warfarin regularly for changes in prothrombin time (PT), INR, or clinical bleeding episodesTemporary interruption of NEXAVAR therapy is recommended in patients undergoing major surgical proceduresIn a subset analysis of two randomized controlled trials in chemo-naÏve patients with Stage IIIB-IV non-small cell lung cancer, patients with squamous cell carcinoma experienced higher mortality with the addition of NEXAVAR compared to those treated with carboplatin/paclitaxel alone (HR 1.81, 95% CI 1.19 – 2.74) and gemcitabine/cisplatin alone (HR 1.22, 95% CI 0.82-1.80). NEXAVAR, in combination with gemcitabine/cisplatin, is not recommended in patients with squamous cell lung cancer. The safety and effectiveness of NEXAVAR has not been established in patients with non-small cell lung cancerNEXAVAR can prolong the QT/QTc interval and increase the risk for ventricular arrhythmias. Avoid use in patients with congenital long QT syndrome and monitor electrolytes and electrocardiograms in patients with congestive heart failure, bradyarrhythmias, drugs known to prolong the QT interval, including Class Ia and III antiarrhythmics, and electrolyte abnormalities. Correct electrolyte abnormalities (magnesium, potassium,calcium). Interrupt NEXAVAR if QTc interval is greater than 500 milliseconds or for an increase from baseline of 60 milliseconds or greaterSorafenib-induced hepatitis is characterized by a hepatocellular pattern of liver damage with significant increases of transaminases which may result in hepatic failure and death. Increases in bilirubin and INR may also occur. Liver function tests should be monitored regularly and in cases of increased transaminases without alternative explanation NEXAVAR should be discontinuedNEXAVAR may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Women of child-bearing potential should be advised to avoid becoming pregnant while on NEXAVARFemale patients should be advised against breastfeeding while receiving NEXAVARIn DTC, NEXAVAR impairs exogenous thyroid suppression. Elevation of thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) level above 0.5 mU/L was observed in 41% of NEXAVAR-treated patients as compared with 16% of placebo-treated patients in the DTC study. For patients with impaired TSH suppression while receiving NEXAVAR, the median maximal TSH was 1.6 mU/L and 25% had TSH levels greater than 4.4 mU/L. Monitor TSH levels monthly and adjust thyroid replacement medication as needed in patients with DTCIn the HCC study, the most common laboratory abnormalities observed in the NEXAVAR arm versus the placebo arm, respectively, were hypoalbuminemia (59% vs. 47%), lymphopenia (47% vs. 42%), thrombocytopenia (46% vs. 41%), elevation in INR (42% vs. 34%), elevated lipase (40% vs. 37%), hypophosphatemia (35% vs. 11%), elevated amylase (34% vs. 29%), hypocalcemia (27% vs. 15%), and hypokalemia (9.5% vs. 5.9%)In the RCC study, the most common laboratory abnormalities observed in the NEXAVAR arm versus the placebo arm, respectively, were hypophosphatemia (45% vs. 11%), anemia (44% vs. 49%), elevated lipase (41% vs. 30%), elevated amylase (30% vs. 23%), lymphopenia (23% vs. 13%), neutropenia (18% vs. 10%), thrombocytopenia (12% vs. 5%), hypocalcemia (12% vs. 8%), and hypokalemia (5.4% vs. 0.7%)In the DTC study, the most common laboratory abnormalities observed in the NEXAVAR arm versus the placebo arm, respectively, were elevated ALT (59% vs. 24%), elevated AST (54% vs. 15%), and hypocalcemia (36% vs. 11%).The relative increase for the following laboratory abnormalities observed in NEXAVAR-treated DTC patients as compared to placebo-treated patients is similar to that observed in the RCC and HCC studies: lipase, amylase, hypokalemia, hypophosphatemia, neutropenia, lymphopenia, anemia, and thrombocytopeniaAvoid concomitant use of strong CYP3A4 inducers, when possible, because inducers can decrease the systemic exposure of sorafenib. NEXAVAR exposure decreases when co-administered with oral neomycin. Effects of other antibiotics on NEXAVAR pharmacokinetics have not been studiedMost common adverse reactions reported for NEXAVAR-treated patients vs placebo-treated patients in unresectable HCC, respectively, were: diarrhea (55% vs. 25%), fatigue (46% vs. 45%), abdominal pain (31% vs. 26%), weight loss (30% vs. 10%), anorexia (29% vs. 18%), nausea (24% vs. 20%), and hand-foot skin reaction (21% vs. 3%). Grade 3/4 adverse reactions were 45% vs. 32%Most common adverse reactions reported for NEXAVAR-treated patients vs placebo-treated patients in advanced RCC, respectively, were: diarrhea (43% vs. 13%), rash/desquamation (40% vs. 16%), fatigue (37% vs. 28%), hand-foot skin reaction (30% vs. 7%), alopecia (27% vs. 3%), and nausea (23% vs. 19%). Grade 3/4 adverse reactions were 38% vs. 28%Most common adverse reactions reported for NEXAVAR-treated patients vs placebo-treated patients in DTC, respectively, were: palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia syndrome (PPES) (69% vs. 8%), diarrhea (68% vs. 15%), alopecia (67% vs. 8%), weight loss (49% vs. 14%), fatigue (41% vs. 20%), hypertension (41% vs. 12%), rash (35% vs. 7%), decreased appetite (30% vs. 5%), stomatitis (24% vs. 3%), nausea (21% vs. 12%), pruritus (20% vs. 11%), and abdominal pain (20% vs. 7%). Grade 3/4 adverse reactions were 65% vs. 30%
药店国别:
产地国家:美国
处方药:是
所属类别: 200毫克/片 120片/瓶
包装规格: 200毫克/片 120片/瓶
计价单位:瓶
生产厂家中文参考译名:
生产厂家英文名:Bayer HealthCare AG
原产地英文商品名:NEXAVAR 200MG/Tablets 120Tablets/bottle
原产地英文药品名:SORAFENIB
中文参考商品译名:多吉美片 200毫克/片 120片/瓶
中文参考药品译名:索拉非尼
曾用名:
简介:部分中文索拉非尼处方资料(仅供参考)英文药名: Nexavar(Sorafenib Tablets)中文药名: 多吉美(索拉非尼片)生产厂家: Bayer Corp.药品名称商品名:多吉美通用名:甲苯磺酸索拉非尼片英文商品名:Nexavar英文通用名:Sorafenib Tablet性状: 本品为红色圆形片。
适应症
索拉非尼已被批准用于治疗晚期肾细胞癌(最常见的肾癌类型)。此外,目前世界各地还有近50项应用索拉非尼治疗其他多种癌症的各类临床试验正在进行之中。
用法用量
索拉非尼为一种红色、薄膜衣片剂,规格为每片200mg。索拉非尼治疗肾细胞癌的推荐剂量为400mg,每天2次,不可与食物同服(宜在进食1小时前或进食2小时后服药)。制药厂商建议,除非索拉非尼疗效降低或患者不能耐受其毒性反应,否则该药可以一直长期使用。若患者出现药物不良反应,索拉非尼给药剂量可降低到400mg,每天1次或隔天1次。任何疑问,请遵医嘱!用药提示患者在服药之前应仔细阅读产品说明书及患者须知。应告知患者在服药期间必须采取有效避孕措施,以及在停药至少2周之后方可尝试怀孕。告知患者最好空腹服药。若患者忘记服药,下一次服药时也无需加大剂量。当患者在服药期间出现手足部皮疹,应及时联络医生进行相应处理。Nexavar是首个获FDA批准专门用于放射性碘(RAI)难治性分化型甲状腺癌的药物2013年11月25日,口服多激酶抑制剂多吉美(Nexavar,通用名:sorafenib,索拉非尼)已获FDA批准,用于局部晚期或转移性放射性碘(RAI)难治性分化型甲状腺癌的治疗。
索拉非尼片英文版说明书
NEXAVAR is indicated for the treatment of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).NEXAVAR is indicated for the treatment of patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC).NEXAVAR is indicated for the treatment of patients with locally recurrent or metastatic, progressive, differentiated thyroid carcinoma (DTC) that is refractory to radioactive iodine treatment.Important Safety ConsiderationsNEXAVAR is contraindicated in patients with known severe hypersensitivity to sorafenib or any other component of NEXAVARNEXAVAR in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel is contraindicated in patients with squamous cell lung cancerCardiac ischemia and/or myocardial infarction may occur. The incidence of cardiac ischemia/infarction in NEXAVAR-treated vs placebo-treated patients was 2.7% vs 1.3%, 2.9% vs 0.4%, and 1.9% vs 0% in the HCC, RCC, and DTC studies, respectively. Temporary or permanent discontinuation of NEXAVAR should be considered in patients who develop cardiac ischemia and/or myocardial infarctionAn increased risk of bleeding may occur following NEXAVAR administration. The following bleeding adverse reactions were reported in the NEXAVAR-treated vs placebo-treated patients, respectively, in the HCC study: bleeding from esophageal varices (2.4% vs 4%) and bleeding with fatal outcome at any site (2.4% vs 4%); in the RCC study: bleeding regardless of causality (15.3% vs 8.2%), Grade 3 bleeding (2.0% vs 1.3%), Grade 4 bleeding (0% vs 0.2%), and one fatal hemorrhage in each treatment group; in the DTC study: bleeding (17.4% vs 9.6%) and Grade 3 bleeding (1% vs 1.4%). There was no Grade 4 bleeding reported and there was one fatal hemorrhage in a placebo-treated patient. If bleeding necessitates medical intervention, consider permanent discontinuation of NEXAVAR. Due to the potential risk of bleeding, tracheal, bronchial, and esophageal infiltration should be treated with local therapy prior to administering NEXAVAR in patients with DTCMonitor blood pressure weekly during the first 6 weeks and periodically thereafter, and treat, if required. In the HCC study, hypertension was reported in approximately 9.4% of NEXAVAR-treated patients and 4.3% of patients in the placebo-treated group. In the RCC study, hypertension was reported in approximately 16.9% of NEXAVAR-treated patients and 1.8% of patients in the placebo-treated group. In the DTC study, hypertension was reported in 40.6% of NEXAVAR-treated patients and 12.4% of the placebo-treated patients. Hypertension was usually mild to moderate, occurred early in the course of treatment, and was managed with standard antihypertensive therapy. In cases of severe or persistent hypertension despite institution of antihypertensive therapy, consider temporary or permanent discontinuation of NEXAVARHand-foot skin reaction and rash are the most common adverse reactions attributed to NEXAVAR. Management may include topical therapies for symptomatic relief. In cases of any severe or persistent adverse reactions, temporary treatment interruption, dose modification, or permanent discontinuation of NEXAVAR should be considered. There have been reports of severe dermatologic toxicities, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN). These cases may be life-threatening. Discontinue NEXAVAR if SJS or TEN are suspectedGastrointestinal perforation was an uncommon adverse reaction and has been reported in less than 1% of patients taking NEXAVAR. Discontinue NEXAVAR in the event of a gastrointestinal perforationInfrequent bleeding or elevations in the International Normalized Ratio (INR) have been reported in some patients taking warfarin while on NEXAVAR. Monitor patients taking concomitant warfarin regularly for changes in prothrombin time (PT), INR, or clinical bleeding episodesTemporary interruption of NEXAVAR therapy is recommended in patients undergoing major surgical proceduresIn a subset analysis of two randomized controlled trials in chemo-naÏve patients with Stage IIIB-IV non-small cell lung cancer, patients with squamous cell carcinoma experienced higher mortality with the addition of NEXAVAR compared to those treated with carboplatin/paclitaxel alone (HR 1.81, 95% CI 1.19 – 2.74) and gemcitabine/cisplatin alone (HR 1.22, 95% CI 0.82-1.80). NEXAVAR, in combination with gemcitabine/cisplatin, is not recommended in patients with squamous cell lung cancer. The safety and effectiveness of NEXAVAR has not been established in patients with non-small cell lung cancerNEXAVAR can prolong the QT/QTc interval and increase the risk for ventricular arrhythmias. Avoid use in patients with congenital long QT syndrome and monitor electrolytes and electrocardiograms in patients with congestive heart failure, bradyarrhythmias, drugs known to prolong the QT interval, including Class Ia and III antiarrhythmics, and electrolyte abnormalities. Correct electrolyte abnormalities (magnesium, potassium,calcium). Interrupt NEXAVAR if QTc interval is greater than 500 milliseconds or for an increase from baseline of 60 milliseconds or greaterSorafenib-induced hepatitis is characterized by a hepatocellular pattern of liver damage with significant increases of transaminases which may result in hepatic failure and death. Increases in bilirubin and INR may also occur. Liver function tests should be monitored regularly and in cases of increased transaminases without alternative explanation NEXAVAR should be discontinuedNEXAVAR may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Women of child-bearing potential should be advised to avoid becoming pregnant while on NEXAVARFemale patients should be advised against breastfeeding while receiving NEXAVARIn DTC, NEXAVAR impairs exogenous thyroid suppression. Elevation of thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) level above 0.5 mU/L was observed in 41% of NEXAVAR-treated patients as compared with 16% of placebo-treated patients in the DTC study. For patients with impaired TSH suppression while receiving NEXAVAR, the median maximal TSH was 1.6 mU/L and 25% had TSH levels greater than 4.4 mU/L. Monitor TSH levels monthly and adjust thyroid replacement medication as needed in patients with DTCIn the HCC study, the most common laboratory abnormalities observed in the NEXAVAR arm versus the placebo arm, respectively, were hypoalbuminemia (59% vs. 47%), lymphopenia (47% vs. 42%), thrombocytopenia (46% vs. 41%), elevation in INR (42% vs. 34%), elevated lipase (40% vs. 37%), hypophosphatemia (35% vs. 11%), elevated amylase (34% vs. 29%), hypocalcemia (27% vs. 15%), and hypokalemia (9.5% vs. 5.9%)In the RCC study, the most common laboratory abnormalities observed in the NEXAVAR arm versus the placebo arm, respectively, were hypophosphatemia (45% vs. 11%), anemia (44% vs. 49%), elevated lipase (41% vs. 30%), elevated amylase (30% vs. 23%), lymphopenia (23% vs. 13%), neutropenia (18% vs. 10%), thrombocytopenia (12% vs. 5%), hypocalcemia (12% vs. 8%), and hypokalemia (5.4% vs. 0.7%)In the DTC study, the most common laboratory abnormalities observed in the NEXAVAR arm versus the placebo arm, respectively, were elevated ALT (59% vs. 24%), elevated AST (54% vs. 15%), and hypocalcemia (36% vs. 11%).The relative increase for the following laboratory abnormalities observed in NEXAVAR-treated DTC patients as compared to placebo-treated patients is similar to that observed in the RCC and HCC studies: lipase, amylase, hypokalemia, hypophosphatemia, neutropenia, lymphopenia, anemia, and thrombocytopeniaAvoid concomitant use of strong CYP3A4 inducers, when possible, because inducers can decrease the systemic exposure of sorafenib. NEXAVAR exposure decreases when co-administered with oral neomycin. Effects of other antibiotics on NEXAVAR pharmacokinetics have not been studiedMost common adverse reactions reported for NEXAVAR-treated patients vs placebo-treated patients in unresectable HCC, respectively, were: diarrhea (55% vs. 25%), fatigue (46% vs. 45%), abdominal pain (31% vs. 26%), weight loss (30% vs. 10%), anorexia (29% vs. 18%), nausea (24% vs. 20%), and hand-foot skin reaction (21% vs. 3%). Grade 3/4 adverse reactions were 45% vs. 32%Most common adverse reactions reported for NEXAVAR-treated patients vs placebo-treated patients in advanced RCC, respectively, were: diarrhea (43% vs. 13%), rash/desquamation (40% vs. 16%), fatigue (37% vs. 28%), hand-foot skin reaction (30% vs. 7%), alopecia (27% vs. 3%), and nausea (23% vs. 19%). Grade 3/4 adverse reactions were 38% vs. 28%Most common adverse reactions reported for NEXAVAR-treated patients vs placebo-treated patients in DTC, respectively, were: palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia syndrome (PPES) (69% vs. 8%), diarrhea (68% vs. 15%), alopecia (67% vs. 8%), weight loss (49% vs. 14%), fatigue (41% vs. 20%), hypertension (41% vs. 12%), rash (35% vs. 7%), decreased appetite (30% vs. 5%), stomatitis (24% vs. 3%), nausea (21% vs. 12%), pruritus (20% vs. 11%), and abdominal pain (20% vs. 7%). Grade 3/4 adverse reactions were 65% vs. 30%
用药温馨提示:当您服用此药物时,需定期接受医疗专业人士的检查,以便随时针对其药效、副作用等情况进行监测。本网站所包含的信息旨在为患者提供帮助,不能代替医学建议和治疗。
药品价格查询,专业药品查询网站,药品说明书查询,药品比价 » 索拉非尼片Nexavar 200mg Tablets(Sorafenib)
药品价格查询,专业药品查询网站,药品说明书查询,药品比价 » 索拉非尼片Nexavar 200mg Tablets(Sorafenib)


