卡莫司汀植入膜剂(GLIADEL WAFER 7.7mg Implant)
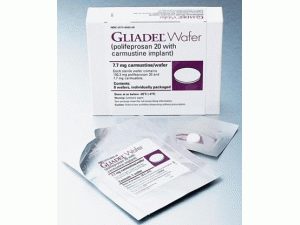 产地国家:美国
产地国家:美国
处方药:是
所属类别: 7.7毫克/片,8片/盒
包装规格: 7.7毫克/片,8片/盒
计价单位:盒
生产厂家英文名:ARBOR PHARMACEUTICALS INC
原产地英文商品名:GLIADEL WAFER IMPLANT DS 8
原产地英文药品名:CARMUSTINE IN POLIFEPROSAN 20
中文参考商品译名:格立得植入剂 7.7毫克/片 8片/包
中文参考药品译名:卡莫司汀
曾用名:卡氮芥、氯乙亚硝脲、亚硝基脲芥
简介:
GLIADEL®WAFER(carmustine implant,中文译名 卡莫司汀植入膜剂)-全球唯一治疗恶性胶质瘤新药近日,FDA批准其治疗脑癌的专利药:以聚苯丙生20为载体的卡莫司汀植入膜剂(polifeprosan 20 with carmustine implant,Gliadel)为罕用药,在治疗接受一期切除术的恶性胶质瘤患者领域享有7年的市场独占期。Gliadel为一种白色至灰白色的一角硬币大小的薄膜,包含生物可降解聚合物聚苯丙生20和7.7mg卡莫司汀(carmustine,BCNU),卡莫司汀是治疗恶性胶质瘤的常用静脉给药的化疗药物。当手术切除脑瘤时,在经手术创建的空腔中可最多植入8片本品。在植入处,Gliadel将缓慢溶解,直接向肿瘤部位释放高浓度卡莫司汀,使扩撒到其它部位的药物减至最少。Gliadel适应证是新诊断为高度恶性胶质瘤的患者的手术和放疗辅助药物,也可作为多形性胶质母细胞瘤(GBM)复发患者的手术辅助用药。批准日期:2012年12月31日 公司:Arbor Pharmaceuticals, LLCGLIADEL®WAFER(卡莫司汀[carmustine implant])植入物,用于颅内使用美国初步批准:1996年
作用机制:GLIADEL晶片的活性是由于释放肿瘤切除腔中的卡莫司汀,DNA和RNA烷基化剂的细胞毒性浓度。 在暴露于切除腔的水环境中,共聚物中的酸酐键被水解,将卡莫司汀,羧基苯氧基丙烷和癸二酸释放到周围的脑组织中。
适用范围及用途:GLIADEL晶片是一种烷基化药物,用于治疗:新诊断的高级恶性胶质瘤作为手术和放射的辅助手段和复发性胶质母细胞瘤多形性作为手术的辅助手段。
剂量和管理:推荐剂量,8毫克7.7毫克晶片(总剂量61.6毫克)植入颅内。遵循准备和处理建议。
剂量形式和强度:每个GLIADEL晶片含有7.7毫克卡莫司汀。
禁忌症:没有
警告和注意事项:(1)癫痫发作:监测患者癫痫发作后的植入。(2)颅内高血压:监测患者颅内压升高的迹象。(3)损伤神经外科伤口愈合:监测患者开颅手术并发症。(4)脑膜炎:监测患者细菌或化学性脑膜炎的症状。(5)晶片移植:监测患者阻塞性脑积水的征兆。(6)胚胎 - 胎儿毒性:可引起胎儿伤害。
不良反应:(1)新诊断的高级恶性胶质瘤:最常见的不良反应(发生率> 10%,手臂差异≥4%)为脑水肿,虚弱,恶心,呕吐,便秘,伤口愈合异常和抑郁。(2)复发性高级恶性胶质瘤:最常见的不良反应(发生率> 10%,手臂差异≥4%)为尿路感染,伤口愈合异常和发烧。
特定人口中使用:儿科用药:安全无效。
储存:存放在-20ºC或以下(-4ºF)。在30天的时间内,不要将未打开的铝箔袋在室温下保持六个小时以上,最多三次。
英文版说明书:
beecDESCRIPTIONGLIADEL® Wafer (polifeprosan 20 with carmustine implant) is a sterile, off-white to pale yellow wafer approximately 1.45 cm in diameter and 1 mm thick. Each wafer contains 192.3 mg of a biodegradable polyanhydride copolymer and 7.7 mg of carmustine [1,3-bis (2-chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea, or BCNU]. Carmustine is a nitrosourea oncolytic agent. The copolymer, polifeprosan 20, consists of poly[bis(p-carboxyphenoxy) propane: sebacic acid] in a 20:80 molar ratio and is used to control the local delivery of carmustine. Carmustine is homogeneously distributed in the copolymer matrix.The structural formula for polifeprosan 20 is:The structural formula for carmustine is:CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGYGLIADEL® Wafer is designed to deliver carmustine directly into the surgical cavity created when a brain tumor is resected. On exposure to the aqueous environment of the resection cavity, the anhydride bonds in the copolymer are hydrolyzed, releasing carmustine, carboxyphenoxypropane, and sebacic acid. The carmustine released from GLIADEL® Wafer diffuses into the surrounding brain tissue and produces an antineoplastic effect by alkylating DNA and RNA.Carmustine has been shown to degrade both spontaneously and metabolically. The production of an alkylating moiety, hypothesized to be chloroethyl carbonium ion, leads to the formation of DNA cross-links.The tumoricidal activity of GLIADEL® Wafer is dependent on release of carmustine to the tumor cavity in concentrations sufficient for effective cytotoxicity.More than 70% of the copolymer degrades by three weeks. The metabolic disposition and excretion of the monomers differ. Carboxyphenoxypropane is eliminated by the kidney and sebacic acid, an endogenous fatty acid, is metabolized by the liver and expired as CO2 in animals.The absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion of the copolymer in humans is unknown. Carmustine concentrations delivered by GLIADEL® Wafer in human brain tissue have not been determined. Plasma levels of carmustine after GLIADEL® Wafer implant were not determined. In rabbits implanted with wafers containing 3.85% carmustine, no detectible levels of carmustine were found in the plasma or cerebrospinal fluid.Following an intravenous infusion of carmustine at doses ranging from 30 to 170 mg/m2, the average terminal half-life, clearance, and steady-state volume of distribution were 22 minutes, 56 mL/min/kg, and 3.25 L/kg, respectively. Approximately 60% of the intravenous 200 mg/m2 dose of 14C-carmustine was excreted in the urine over 96 hours and 6% was expired as CO2.GLIADEL® Wafers are biodegradable in human brain when implanted into the cavity after tumor resection. The rate of biodegradation is variable from patient to patient. During the biodegradation process, a wafer remnant may be observed on brain imaging scans or at re-operation even though extensive degradation of all components has occurred. Data obtained from review of CT scans obtained 49 days after implantation of GLIADEL® Wafer demonstrated that images consistent with wafers were visible to varying degrees in the scans of 11 of 18 patients. Data obtained at re-operation and autopsies have demonstrated wafer remnants up to 232 days after GLIADEL® Wafer implantation.Wafer remnants removed at re-operation from two patients with recurrent malignant glioma, one at 64 days and the second at 92 days after implantation, were analyzed for content. The following table presents the results of analyses completed on these remnants.COMPOSITION OF WAFER REMNANTS REMOVED FROM TWO PATIENTS ON RE-OPERATIONThe wafer remnants consisted mostly of water and monomeric components with minimal detectable carmustine present.CLINICAL STUDIESPrimary SurgeryA randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial was conducted in adult patients with newly-diagnosed high-grade malignant glioma undergoing initial craniotomy for tumor resection. This trial determined the safety and efficacy of GLIADEL® Wafer implants plus surgery and radiation therapy compared to placebo implants plus surgery and radiation therapy. Two hundred and forty patients with newly-diagnosed malignant glioma were enrolled. The most common tumor type was Glioblastoma Multiforme (GBM) (n=207), followed by anaplastic oligoastrocytoma (n=11), anaplastic oligodendroglioma (n=11), and anaplastic astrocytoma (n=2). GLIADEL® Wafers were implanted at the time of the surgery in 120 patients and placebo wafers were implanted in 120 patients. The majority of patients received 6-8 wafers. The majority of patients (93/120, 77.5% in the GLIADEL® Wafer group and 98/120, 81.7% in the placebo group) with newly-diagnosed malignant glioma received a standard course of radiotherapy (55 to 60 Gy) typically starting 3 weeks after surgery. There were 17 patients (14.2%) in the GLIADEL® Wafer group and 12 patients (10.0%) in the placebo group who received systemic chemotherapy during the study. All six patients with anaplastic oligodendroglioma received chemotherapy within 30 days of GLIADEL® Wafer implantation. Patients were followed for at least three years or until death. Only one patient was lost to follow-up. Median survival increased from 11.6 months with placebo to 13.8 months with GLIADEL® Wafer (p-value <0.05, log-rank test). The hazard ratio for GLIADEL® Wafer treatment was 0.73 (95% CI: 0.56-0.95).Kaplan-Meier Overall Survival Curves for Patients Undergoing Initial Surgery for a High-Grade Malignant GliomaWhen only patients with Glioblastoma multiforme were included in the analysis, the hazard ratio with GLIADEL® Wafer treatment was 0.78 (95% CI: 0.59-1.03, p=0.08, log-rank test).Surgery for Recurrent DiseaseA randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial was conducted in adult patients with recurrent malignant glioma. This trial determined the safety and efficacy of GLIADEL® Wafer implants plus surgery compared to placebo implants plus surgery.Ninety-five percent of the patients treated with GLIADEL® Wafer had 7-8 wafers implanted. Chemotherapy was withheld at least four weeks (six weeks for nitrosoureas) prior to and two weeks after surgery in patients undergoing re-operation for malignant glioma. In 222 patients with recurrent malignant glioma who had failed initial surgery and radiation therapy, the six-month survival rate after repeat surgery increased from 47% (53/112) for patients receiving placebo to 60% (66/110) for patients treated with GLIADEL® Wafer. Median survival increased by 33%, from 24 weeks (5.5 months) with placebo to 32 weeks (7.4 months) with GLIADEL® Wafer treatment. In patients with GBM, the six-month survival rate increased from 36% (26/73) with placebo to 56% (40/72) with GLIADEL® Wafer treatment. Median survival of GBM patients increased by 41% from 20 weeks (4.6 months) with placebo to 28 weeks (6.4 months) with GLIADEL® Wafer treatment. In patients with pathologic diagnoses other than GBM at the time of surgery for tumor recurrence, GLIADEL® Wafer produced no survival prolongation.6-MONTH KAPLAN-MEIER SURVIVAL CURVES FOR PATIENTS UNDERGOING SURGERY FOR RECURRENT GBMKAPLAN-MEIER OVERALL SURVIVAL CURVES FOR PATIENTS UNDERGOING SURGERY FOR RECURRENT GBMINDICATIONS AND USAGEGLIADEL® Wafer is indicated in newly-diagnosed high-grade malignant glioma patients as an adjunct to surgery and radiation. GLIADEL® Wafer is indicated in recurrent glioblastoma multiforme patients as an adjunct to surgery.CONTRAINDICATIONSGLIADEL® Wafer contains carmustine. GLIADEL® Wafer should not be given to individuals who have demonstrated a previous hypersensitivity to carmustine or any of the components of GLIADEL® Wafer.WARNINGSPatients undergoing craniotomy for malignant glioma and implantation of GLIADEL® Wafer should be monitored closely for known complications of craniotomy, including seizures, intracranial infections, abnormal wound healing, and brain edema. Cases of intracerebral mass effect unresponsive to corticosteroids have been described in patients treated with GLIADEL® Wafer, including one case leading to brain herniation.Pregnancy: There are no studies assessing the reproductive toxicity of GLIADEL® Wafer. Carmustine, the active component of GLIADEL® Wafer, can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Carmustine has been shown to be embryotoxic and teratogenic in rats at i.p. doses of 0.5, 1, 2, 4, or 8 mg/kg/day when given on gestation days 6 through 15. Carmustine caused fetal malformations (anophthalmia, micrognathia, omphalocele) at 1.0 mg/kg/day (about 1/6 the recommended human dose (eight wafers of 7.7 mg carmustine/wafer) on a mg/m2 basis). Carmustine was embryotoxic in rabbits at i.v. doses of 4.0 mg/kg/day (about 1.2 times the recommended human dose on a mg/m2 basis). Embryotoxicity was characterized by increased embryo-fetal deaths, reduced numbers of litters, and reduced litter sizes.There are no studies of GLIADEL® Wafer in pregnant women. If GLIADEL® Wafer is used during pregnancy, or if the patient becomes pregnant after GLIADEL® Wafer implantation, the patient must be warned of the potential hazard to the fetus.PRECAUTIONSGeneralCommunication between the surgical resection cavity and the ventricular system should be avoided to prevent the wafers from migrating into the ventricular system and causing obstructive hydrocephalus. If a communication larger than the diameter of a wafer exists, it should be closed prior to wafer implantation.Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging of the head may demonstrate enhancement in the brain tissue surrounding the resection cavity after implantation of GLIADEL® Wafers. This enhancement may represent edema and inflammation caused by GLIADEL® Wafer or tumor progression.Therapeutic InteractionsInteractions of GLIADEL® Wafer with other drugs have not been formally eva luated.The short-term and long-term toxicity profiles of GLIADEL® Wafer when given in conjunction with chemotherapy have not been fully explored. GLIADEL® Wafer, when given in conjunction with radiotherapy does not appear to have any short-term or chronic toxicities.Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of FertilityNo carcinogenicity, mutagenicity or impairment of fertility studies have been conducted with GLIADEL® Wafer. Carcinogenicity, mutagenicity and impairment of fertility studies have been conducted with carmustine, the active component of GLIADEL® Wafer. Carmustine was given three times a week for six months, followed by 12 months observation, to Swiss mice at i.p. doses of 2.5 and 5.0 mg/kg (about 1/5 and 1/3 the recommended human dose (eight wafers of 7.7 mg carmustine/wafer) on a mg/m2 basis) and to SD rats at i.p. dose of 1.5 mg/kg (about 1/4 the recommended human dose on a mg/m2 basis). There were increases in tumor incidence in all treated animals, predominantly subcutaneous and lung neoplasms. Mutagenesis: Carmustine was mutagenic in vitro (Ames assay, human lymphoblast HGPRT assay) and clastogenic both in vitro (V79 hamster cell micronucleus assay) and in vivo (SCE assay in rodent brain tumors, mouse bone marrow micronucleus assay). Impairment of Fertility: Carmustine caused testicular degeneration at i.p. doses of 8 mg/kg/week for eight weeks (about 1.3 times the recommended human dose on a mg/m2 basis) in male rats.PregnancyPregnancy Category D: see WARNINGS.Nursing MothersIt is not known if either carmustine, carboxyphenoxypropane, or sebacic acid is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions from carmustine in nursing infants, it is recommended that patients receiving GLIADEL® Wafer discontinue nursing.Pediatric UseThe safety and effectiveness of GLIADEL® Wafer in pediatric patients have not been established.ADVERSE REACTIONSAdverse reactions for the trials are described in the tables below.Primary SurgeryThe following data are the most frequently occurring adverse events observed in 5% or more of the newly-diagnosed malignant glioma patients during the trial.COMMON ADVERSE EVENTS OBSERVED IN ≥ 5% OF PATIENTS RECEIVING GLIADEL® WAFER AT INITIAL SURGERYAdverse events coded to the COSTART term "aggravation reaction" were usually events involving tumor/disease progression or general deterioration of condition (e.g. condition/health/Karnofsky/neurological/physical deterioration).Surgery for Recurrent DiseaseThe following post-operative adverse events were observed in 4% or more of the patients receiving GLIADEL® Wafer at recurrent surgery. Except for nervous system effects, where there is a possibility that the placebo wafers could have been responsible, only events more common in the GLIADEL® Wafer group are listed. These adverse events were either not present pre-operatively or worsened post-operatively during the follow-up period. The follow-up period was up to 71 months.COMMON ADVERSE EVENTS OBSERVED IN ≥ 4% OF PATIENTS RECEIVING GLIADEL® WAFER AT SURGERY FOR RECURRENT DISEASEp < 0.05 for comparison of GLIADEL® Wafer versus placebo groupsPost-marketing experience includes spontaneous reports of cyst formation after GLIADEL® wafer implantation. These occurred at varying time intervals post-implantation. Cyst formation has also been reported in patients following resection of malignant glioma who have not had Gliadel® implanted.The following four categories of adverse events are possibly related to treatment with GLIADEL® Wafer. The frequency with which they occurred in the randomized trials along with descriptive detail is provided below.1. Seizures: In the initial surgery trial, the incidence of seizures was 33.3% in patients receiving GLIADEL® Wafer and 37.5% in patients receiving placebo. Grand mal seizures occurred in 5% of GLIADEL® Wafer-treated patients and 4.2% of placebo treated patients. The incidence of seizures within the first 5 days after wafer implantation was 2.5% in the GLIADEL® Wafer group and 4.2% in the placebo group. The time from surgery to the onset of the first post-operative seizure did not differ between the GLIADEL® Wafer and placebo treated patients.In the surgery for recurrent disease trial, the incidence of post-operative seizures was 19% in both patients receiving GLIADEL® Wafer and placebo. In this study, 12/22 (54%) of patients treated with GLIADEL® Wafer and 2/22 (9%) of placebo patients experienced the first new or worsened seizure within the first five post-operative days. The median time to onset of the first new or worsened post-operative seizure was 3.5 days in patients treated with GLIADEL® Wafer and 61 days in placebo patients.2. Brain Edema: In the initial surgery trial, brain edema was noted in 22.5% of patients treated with GLIADEL® Wafer and in 19.2% of patients treated with placebo. Development of brain edema with mass effect (due to tumor recurrence, intracranial infection, or necrosis) may necessitate re-operation and, in some cases, removal of GLIADEL® Wafer or its remnants.3. Healing Abnormalities: The following healing abnormalities have been reported in clinical trials of GLIADEL® Wafer: wound dehiscence, delayed wound healing, subdural, subgaleal or wound effusions, and cerebrospinal fluid leak. In the initial surgery trial, healing abnormalities occurred in 15.8% of GLIADEL® Wafer treated patients and in 11.7% of placebo recipients. Cerebrospinal fluid leaks occurred in 5% of GLIADEL® Wafer recipients and 0.8% of those given placebo. During surgery, a water-tight dural closure should be obtained to minimize the risk of cerebrospinal fluid leak.In the surgery for recurrent disease trial, the incidence of healing abnormalities was 14% in GLIADEL® Wafer treated patients and 5% in patients receiving placebo wafers.4. Intracranial Infection: In the initial surgery trial, the incidence of brain abscess or meningitis was 5% in patients treated with GLIADEL® Wafer and 6% in patients receiving placebo. In the recurrent setting, the incidence of brain abscess or meningitis was 4% in patients treated with GLIADEL® Wafer and 1% in patients receiving placebo.The following adverse events, not listed in the table above, were reported in less than 4% but at least 1% of patients treated with GLIADEL® Wafer in all studies. The events listed were either not present pre-operatively or worsened post-operatively. Whether GLIADEL® Wafer caused these events cannot be determined.Body as a Whole: peripheral edema (2%); neck pain (2%); accidental injury (1%); back pain (1%); allergic reaction (1%); asthenia (1%); chest pain (1%); sepsis (1%)Cardiovascular System: hypertension (3%); hypotension (1%)Digestive System: diarrhea (2%); constipation (2%); dysphagia (1%); gastrointestinal hemorrhage (1%); fecal incontinence (1%)Hemic and Lymphatic System: thrombocytopenia (1%); leukocytosis (1%)Metabolic and Nutritional Disorders: hyponatremia (3%); hyperglycemia (3%); hypokalemia (1%)Musculoskeletal System: infection (1%)Nervous System: hydrocephalus (3%); depression (3%); abnormal thinking (2%); ataxia (2%); dizziness (2%); insomnia (2%); monoplegia (2%); coma (1%); amnesia (1%); diplopia (1%); paranoid reaction (1%). In addition, cerebral hemorrhage and cerebral infarct were each reported in less than 1% of patients treated with GLIADEL® Wafer.Respiratory System: infection (2%); aspiration pneumonia (1%)Skin and Appendages: rash (2%)Special Senses: visual field defect (2%); eye pain (1%)Urogenital System: urinary incontinence (2%)OVERDOSAGEThere is no clinical experience with use of more than eight GLIADEL® Wafers per surgical procedure.DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATIONEach GLIADEL® Wafer contains 7.7 mg of carmustine, resulting in a dose of 61.6 mg when eight wafers are implanted. It is recommended that eight wafers be placed in the resection cavity if the size and shape of it allows. Should the size and shape not accommodate eight wafers, the maximum number of wafers as allowed should be placed. Since there is no clinical experience, no more than eight wafers should be used per surgical procedure.Handling and Disposal1-7: Wafers should only be handled by personnel wearing surgical gloves because exposure to carmustine can cause severe burning and hyperpigmentation of the skin. Use of double gloves is recommended and the outer gloves should be discarded into a biohazard waste container after use. A surgical instrument dedicated to the handling of the wafers should be used for wafer implantation. If repeat neurosurgical intervention is indicated, any wafer or wafer remnant should be handled as a potentially cytotoxic agent.GLIADEL® Wafer should be handled with care. The aluminum foil laminate pouches containing GLIADEL® Wafer should be delivered to the operating room and remain unopened until ready to implant the wafers. The outside surface of the outer foil pouch is not sterile.Instructions for Opening Pouch Containing GLIADEL® WaferFigure 1: To remove the sterile inner pouch from the outer pouch, locate the folded corner and slowly pull in an outward motion.Figure 2: Do NOT pull in a downward motion rolling knuckles over the pouch. This may exert pressure on the wafer and cause it to break.Figure 3: Remove the inner pouch by grabbing hold of the crimped edge and pulling upward.Figure 4: To open the inner pouch, gently hold the crimped edge and cut in an arc-like fashion around the wafer.Figure 5: To remove the GLIADEL® Wafer, gently grasp the wafer with the aid of forceps and place it onto a designated sterile field.Once the tumor is resected, tumor pathology is confirmed, and hemostasis is obtained, up to eight GLIADEL® Wafers (polifeprosan 20 with carmustine implant) may be placed to cover as much of the resection cavity as possible. Slight overlapping of the wafers is acceptable. Wafers broken in half may be used, but wafers broken in more than two pieces should be discarded in a biohazard container. Oxidized regenerated cellulose (Surgicel®) may be placed over the wafers to secure them against the cavity surface. After placement of the wafers, the resection cavity should be irrigated and the dura closed in a water tight fashion.Unopened foil pouches may be kept at ambient room temperature for a maximum of six hours at a time.HOW SUPPLIEDGLIADEL® Wafer is available in a single dose treatment box containing eight individually pouched wafers. Each wafer contains 7.7 mg of carmustine and is packaged in two aluminum foil laminate pouches. The inner pouch is sterile and is designed to maintain product sterility and protect the product from moisture. The outer pouch is a peelable overwrap. The outside surface of the outer pouch is not sterile.GLIADEL® Wafer must be stored at or below -20°C (-4°F).
药品价格查询,专业药品查询网站,药品说明书查询,药品比价 » 卡莫司汀植入膜剂(GLIADEL WAFER 7.7mg Implant)